Does urgent care test for STDs? Everything you need to know
Written by Sarah Thebarge, Physician Assistant and medically reviewed by Dr. Betsy Koickel, MD on May 14th, 2025.
If you’re sexually active, getting tested for sexually transmitted diseases/infections (aka STDs or STIs) is crucial to your overall health. Teens and those under 25 are especially at risk for contracting STDs, but anyone sexually active is at risk.
The statistics are quite eye-opening — it’s estimated that one in two sexually active people will contract at least one of the most common STDs by age 25. Over 2.4 million cases of syphilis, gonorrhea and chlamydia were reported in 2023 by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
What many people don’t know is that STD testing is widely available. You’re not limited to specialty clinics for STD testing. In fact, you can just walk into most urgent cares for STD testing at any time.
STD vs. STI
STD stands for sexually transmitted diseases, and STI stands for sexually transmitted infections. While these terms are sometimes used interchangeably to refer to any sexually transmitted illness, they are not quite the same.
An STI is an infection caused by a virus, bacteria or parasite contracted via sexual contact. This is the early stage of the illness that has not yet developed into a more serious disease. If an STI is diagnosed and treated early, it may only cause mild symptoms.
STDs are diseases that start as STIs but have begun to disrupt normal body functions and may have more severe symptoms.
A good example of the difference between STIs and STDs is the human papillomavirus (HPV). Many people are carriers of HPV but show no symptoms. This would be considered an STI. If the HPV infection develops into genital warts, this would then be considered a more serious STD.
Urgent care STD testing procedure
Even if you don’t have any symptoms of sexually transmitted diseases, it’s a good idea to get tested if you’ve had unprotected sex.
Also, if you use protection but have multiple partners, getting tested for your and your partners' safety and peace of mind is a good idea.
Testing for STDs is just like getting tested in any other clinical setting. Your medical provider first evaluates you for symptoms that may suggest an STD infection and then runs tests based on what they find during the examination. A physical exam is usually required, which can sometimes include a pelvic exam for females.
Depending on your symptoms, your provider may draw blood or take a urine sample. In other cases, the provider will use a swab to collect a sample from the affected area.
Cost of STD testing at urgent care
It’s hard to say exactly how much an STD test will cost, as your co-pay fluctuates depending on insurance. Based on the initial consultation, the total out-of-pocket cost will also be determined by how many tests you need.
On average, most pay between $50-100 for initial testing if their insurance is in-network with their medical provider.
Establishing a gynecologist for annual check-ups and screenings is highly recommended. They can help female patients look into birth control options, as well as provide STD testing that is typically covered by most insurance plans.
Don’t think you are off the hook, gentlemen! You should also look into annual screenings and regular check-ups between partners.
When to get tested for STDs
If you are not sure when you need to visit urgent care for STD testing, here are some situations when you might want to consider visiting one of our convenient centers:
- Any time after you have unprotected sex, you should get tested one to two weeks later and then again 90 days later.
- If you exhibit any symptoms of STDs (change in discharge- color, more copious, or odorous, burning sensation while urinating, pelvic pain, or pain with intercourse).
- Annually, if you’re a woman under 25 (specifically for chlamydia, during a well visit).
- Annually, if you’re sexually active and not in a mutually monogamous relationship.
- Pregnant women who may or may not be experiencing symptoms should be tested for chlamydia and syphilis, regardless of their sexual history.
STD symptoms
Symptoms of STDs can vary based on the particular illness and may be experienced differently by women and men. If you are ever concerned that one of your symptoms might be an STD, it is best to get tested.
Symptoms in women
Common STD symptoms in women:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding
- Burning or pain with urination or bowel movements
- Discharge or odor from the vaginaI
- Itching or burning in the vaginal area
- Needing to go to the bathroom often
- Pelvic pain
- Pain during intercourse
- Sores, bumps, blisters or warts in the vagina, anus or mouth
Symptoms in men
Common STD symptoms in men may include:
- Burning or pain with urination or bowel movements
- Discharge from the penis
- Itching or burning around or inside the penis
- Needing to go to the bathroom often
- Pelvic pain
- Sores, bumps, blisters or warts on the penis, urethra, anus or mouth
How long does an STD take to show up?
If you have been exposed to an STD, you might be thinking, when do symptoms of STDs start? When symptoms start, they can vary depending on the illness. Most will appear within two to three weeks of transmission, but some can take up to six weeks. This is why STD testing is recommended around two to four weeks after potential exposure.
Keep in mind even if you do not have symptoms, you may still be able to transmit the disease to others, so you may want to take precautions or avoid sexual contact until you can get tested.
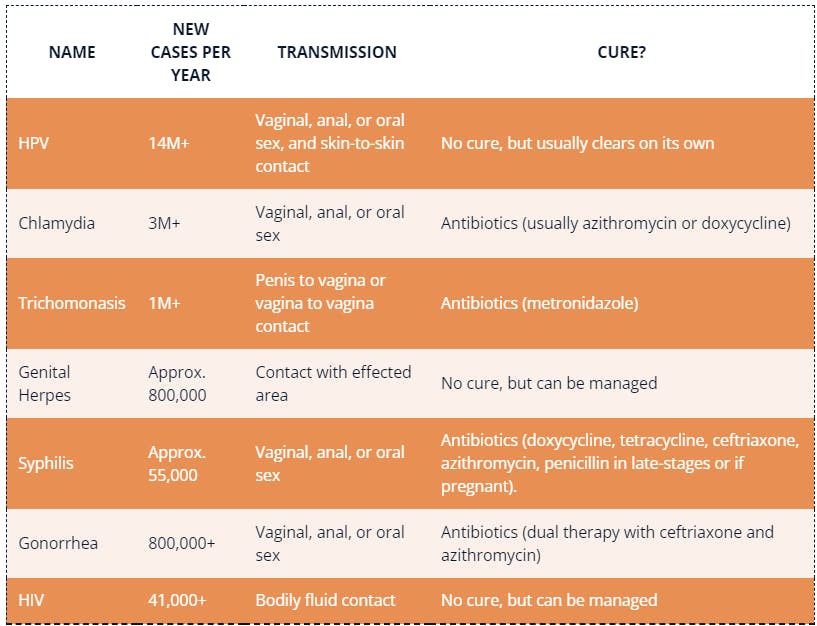
Most common STDs
The seven most common STDs vary in terms of seriousness and treatment options. Infections like chlamydia and trichomoniasis are easily taken care of by antibiotics, whereas an infection like genital herpes can be managed but never entirely cured.
HPV, chlamydia and trichomoniasis are the most common STDs in the United States. HPV and chlamydia are most common in men and women under the age of 25.
HPV infection can be particularly concerning for women, as it increases their risk for cervical cancer. Trichomoniasis is a vaginal infection that also primarily affects young women.
Here are the details about the most common STDs, symptoms to look for and treatments in men and women:
Genital Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
Without a doubt, HPV is the single most frequently occurring STD. It’s spread through oral, anal and vaginal sex. It can also be spread by skin-to-skin contact, though the infection typically inhabits the genitals, mouth or throat. Most of the time, women with HPV are unaware they have it. In most cases, no symptoms are present.
HPV is especially common in women. Although the infection usually clears on its own within two years, this isn’t always the case. Major complications can arise if the body does not rid itself of the virus. Some strains can lead to problems like genital warts and cervical cancer.
Treatment
Screening for HPV during a pap smear is the best way to determine if further treatment is needed or if the virus will clear on its own.
The good news is that the dangerous strains of HPV can be prevented with a vaccine. It is recommended that boys and girls get vaccinated for HPV at 11 years old. The vaccine should be administered twice, six to 12 months apart. If the person was not vaccinated when they were younger, it’s ideal to get vaccinated if you’re under 26.
Chlamydia
Similar to HPV, chlamydia is a highly prevalent STD that often doesn’t show any signs or symptoms. The infection develops about one to three weeks after the initial exposure, and it’s contracted through oral, vaginal or anal sex. With only about 25% of women experiencing symptoms (while 50% of men report experiencing symptoms), making well visits vital for prevention and limiting other exposure.
Symptoms can include:
- Abnormal discharge from the penis
- Bleeding between menstrual cycles
- Burning sensation in the penis
- Inflamed eye
- Pain during sex
- Painful urination
- Rectal pain or discharge
- Testicular pain and swelling
- Vaginal discharge
Treatment
Chlamydia is easily treated with a seven-day course of antibiotics. If left untreated, it can lead to many reproductive problems for women. The infection can move upward to the uterus and fallopian tubes, possibly leading to infertility. Chlamydia is most prevalent in women ages 15- 24, so make sure to schedule an STD check annually if you fall within that age range.
Trichomoniasis
An infection caused by a parasite, trichomoniasis is a common STD that causes few symptoms to indicate infection. The infection is spread from a penis to a vagina or from a vagina to a vagina. It’s rare for the infection to affect other body parts like the hands or mouth.
About 70% of infected people do not show any symptoms, but some symptoms occur within five to 28 days after being infected.
Symptoms can include:
- Burning after urinating
- Burning, soreness or itching of the genitals
- Colored vaginal discharge with an unusual smell
- Discharge originating from the penis
- Discomfort while urinating
- Itching or irritating inside the penis
Treatment
Luckily, trichomoniasis is considered the most curable STD. Medical providers will prescribe antibiotics, which should clear the infection. An infected person can use a cold compress on the infected area to relieve symptoms.
Gonorrhea
Any sexually active person can contract gonorrhea by having vaginal, anal or oral sex with an infected person. It can also be passed on from a pregnant woman to her baby during birth.
Sometimes referred to as “the clap” or “the drip,” gonorrhea often, but not always, shows symptoms. While symptoms for men are expected, many women with gonorrhea do not have any symptoms. Or, if symptoms are present in infected women, they tend to be mild and can be mistaken for a UTI.
Symptoms of gonorrhea include:
- Bleeding between menstrual cycles
- Burning sensation during urination
- Colored discharge from the penis
- Increased vaginal discharge
Treatment
Usually, a urine sample is used when testing for gonorrhea. However, if applicable, a swab may be used to collect samples from the throat or rectum. Gonorrhea is usually curable with antibiotics; however, drug-resistant strains of gonorrhea have increased in recent years.
Genital herpes
Genital herpes is a common STD with about one in six Americans carrying the disease. Up to 90% of people infected with the disease are unaware they have it. It can take as little as a few days after sexual contact to develop symptoms. There is no universal rule as to how fast herpes develops and progresses.
Typically, infected persons experience genital herpes in episodes. The initial outbreak is marked by sores, vesicles or ulcers known as “lesions.” They look similar to zits or blisters. Some people experience incredibly painful lesions, whereas others might experience lesions so mild it can be mistaken for a yeast infection or jock itch. In more extreme cases, an infected person may also experience flu-like symptoms like fever and headache.
After the first episode, the severity of symptoms tends to decrease. Lesions will become less pronounced and less painful with time. Since genital herpes specifically inhabits the nerves surrounding the spine, outbreaks will usually occur in the upper thighs, buttocks and genitals. Lesions will not occur on the face. Sometimes, factors like illness, stress and friction will trigger outbreaks in an affected person.
Treatment
Unfortunately, genital herpes is an incurable condition; however, it can be managed with antiviral treatments.
The best way to avoid herpes is through prevention. Genital herpes is spread through vaginal, anal and oral sex with an infected person. The fluids found in herpes lesions carry the virus. Even with a condom, the disease can be spread by parts of the body that are left uncovered.
Rarely, herpes can cause inflammation of the brain, liver and other organs during the initial infection. If you suspect that you have contracted genital herpes, you should get evaluated at the time of the rash to confirm the diagnosis.
Syphilis
Syphilis is easily cured by antibiotics, but it can lead to serious health problems if left untreated. As syphilis affects the body in stages, depending on how long it’s left untreated, certain damage can’t be reversed.
Any sexually active person can contract syphilis via vaginal, anal or oral sex. It’s spread via sores that occur on or around the penis, vagina, anus, rectum, lips or mouth. Also, it can be passed from mother to child during birth.
4 stages of syphilis in adults
- One or more sores are located where the disease entered your body. Usually, this stage is relatively painless and persists for three to six weeks. The sore will heal, but that does not mean the disease is cured. This is the natural progression to the following stage.
- Secondary stage: A red or reddish-brown rash starts in one or more areas of your body. Typically, the rash doesn’t itch, but other symptoms can include fever, sore throat, headaches and weight loss. Without treatment, the symptoms will disappear and proceed to the next stages.
- If left untreated, syphilis will seemingly disappear and show no symptoms for some time. This stage can last for years until symptoms occur in the next stage.
- Tertiary stage: At this stage, syphilis affects organ systems like the cardiovascular and nervous systems. The tertiary stage is incredibly serious, occurs approximately ten to 30 years after the initial infection and can result in death.
Treatment
Syphilis is curable with antibiotics. Getting tested as early as possible and starting treatment immediately is important to avoid more serious complications.
HIV
The HIV/AIDS epidemic of the 90s terrified the world. While we don’t have a cure yet, many people live long lives with HIV. Awareness is also more common these days than it was in the 90s, and there are many more resources around these days as well.
HIV is a virus that destroys white blood cells, which are a critical part of the immune system. White blood cells fight off harmful viruses, so HIV harms the body by weakening a person’s immune system. When the immune system is compromised, other serious diseases can develop and jeopardize your health.
Stages of HIV
After contracting HIV, the disease moves in stages if left untreated.
- One to four weeks after contracting the virus, many people experience flu-like symptoms like fever, swollen glands, headache, sore throat and muscle pain.
- Asymptomatic stage: After the initial stage, many people begin to feel better and can be symptom-free for ten to 15 years. However, even if no symptoms are present, the disease can still cause damage to a person’s immune system.
- At this stage, a person is said to have acquired immune deficiency syndrome or AIDS. The body is vulnerable to many types of infections that it could ordinarily fight off.
Early HIV signs and symptoms may include:
- Fatigue
- Fever and chills
- Headache
- Sore throat
- Swollen lymph glands — usually one of the first signs of an HIV infection
- Rash
Late-stage HIV infection symptoms include:
- Chronic diarrhea
- Extremely swollen lymph nodes
- Prolonged fevers, sometimes lasting weeks with temperatures of more than 100.4 F (38 C)
- Night sweats and chills
- Persistent fatigue
- Persistent headaches and migraines
Treatment
Fortunately, new advances in medicine can allow people diagnosed with HIV to live long, productive lives; however, the disease is still not curable and, if left untreated, can develop into AIDS.
The best prevention method is by properly using condoms whenever engaging in anal or vaginal sex. Keep in mind that oil-based lubricants can weaken condoms, so it’s best to stick to water-based lubricants. HIV is spread by bodily fluid contact, so transmitting the virus is most likely during sexual contact or when sharing needles to inject drugs. Women with HIV may pass the infection to the baby during childbirth.
Wrapping it up
The most important takeaway here is to use protection. Although STDs range in seriousness and treatability, taking the proper preventative measures is your best bet. Male and female condoms do not eliminate the transmission of STDs, but they can significantly reduce the chances of all STDs.
If you experience any symptoms of an STD after a sexual encounter, you should abstain from sex until you can get tested. In addition, be sure to tell any past partners to prevent spreading STDs before your diagnosis. STD testing is easy and can usually be done at your local urgent care center. Most STDs can be treated or at least significantly reduced in severity with the proper medication.
We can’t stress it enough: use protection to prevent STDs! For more information regarding STD prevention or the risks of becoming infected, visit the CDC website.
We offer STD tests and other tests for your medical needs, with no appointment necessary. We are open every day with extended hours, making it easy for you to come in after work, on lunch or whenever is convenient.
FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about urgent care STD testing:
Does urgent care test for STDs?
Yes, we can offer consultations, testing and treatment for STDs.
How long do STD test results take from urgent care?
The test results will depend on the type of STD you have. Some tests can be completed in the office, whereas some may need to be sent out for results.
Do I need an appointment for STD testing at urgent care?
No, you can walk into any urgent care center or save your spot online if you prefer not to wait.
Does urgent care do STI testing?
Yes, we can offer consultations, testing and treatment for STIs.
Is STD testing at urgent care covered by insurance?
Most health insurance will cover STD testing, but the amount covered will depend on your plan.
What should I do if I test positive for an STD?
If you test positive for an STD, be sure to follow the treatment plan outlined by your healthcare provider. You should also talk to anyone you have had sexual contact with and encourage them to get tested and treated as well.
Can I get treated for an STD at urgent care?
Yes, you can get STD testing and treatment at urgent care.
What is the most common STD?
The most common STD is human papillomavirus (HPV).
How accurate are STD tests at urgent care?
The accuracy of an STD test can depend on the timing of the exposure and the type of test. A healthcare provider will discuss your options and do a physical exam to determine the best test for your symptoms.
How often should I get tested for STDs?
The CDC emphasizes the importance of STD testing. They recommend annual STD testing for anyone who is sexually active and not in a monogamous relationship. More frequent testing is recommended for people with multiple or anonymous partners.
References:
- https://www.cdc.gov/hpv/index.html
- https://www.cdc.gov/sti/about/?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/std/general/default.htm
- https://www.cdc.gov/sti/about/about-genital-hpv-infection.html?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/std/hpv/stdfact-hpv.htm
- https://www.cdc.gov/trichomoniasis/about/index.html
- https://www.webmd.com/sex/how-common-genital-herpes
- https://www.cdc.gov/syphilis/about/index.html
- https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/index.html
- https://thestiproject.com/how-to-tell-someone-you-have-an-std/
- https://www.cdc.gov/sti/prevention/?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/std/prevention
- https://www.cdc.gov/std/treatment-guidelines/screening-recommendations.htm